Revolutionizing Energy Storage
Energy storage is the backbone of a sustainable energy future, enabling reliable use of renewable energy. Advancements in storage technologies improve grid stability and support decarbonization.
Battery Storage
Lithium-ion batteries are revolutionizing energy storage by offering high efficiency and energy density, making them essential for applications like renewable energy integration and electric vehicles. These batteries store excess energy generated from renewable sources such as solar and wind, providing power during periods of low generation or high demand. This capability ensures a stable energy supply and reduces reliance on fossil fuels for backup power. With ongoing advancements, lithium-ion technology is becoming more cost-effective, efficient, and crucial for creating a sustainable, low-carbon energy future.
Pumped Hydroelectric Storage
Pumped Hydroelectric Storage is a proven and reliable method of energy storage that harnesses the power of water to balance supply and demand. In this system, water is pumped from a lower reservoir to a higher one during periods of low energy demand, using excess electricity. When demand peaks, the stored water is released back down through turbines, generating electricity to meet the increased demand. This process offers a highly efficient and flexible solution for stabilizing the grid, making it an essential part of energy storage, particularly in regions with abundant water resources.
Compressed Air Storage
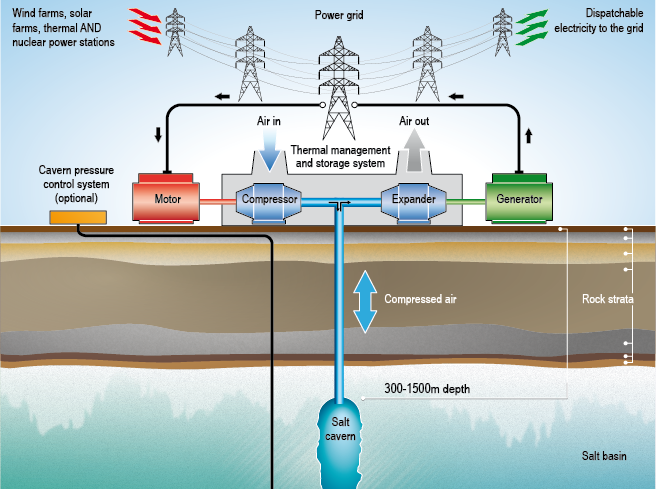
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) is an emerging and scalable solution for energy storage that stores electricity by compressing air and storing it in underground caverns or tanks. During periods of low electricity demand, excess power is used to compress the air, which is then released and heated when demand rises. The expanding air drives turbines to generate electricity. CAES offers a cost-effective and reliable way to store large amounts of energy, making it a promising solution for balancing grid supply and demand, particularly for renewable energy sources like wind and solar.
Thermal Energy Storage

Thermal Energy Storage (TES) involves capturing and storing heat for later use, helping to reduce energy consumption during peak demand periods. One common method is using molten salt, which absorbs and retains heat for extended periods. When needed, the stored heat is released to generate electricity or provide heating. Another method involves storing energy in ice, which can be used for cooling purposes during high-demand hours. TES systems are valuable for enhancing grid stability and improving energy efficiency, especially in combination with renewable energy sources, by shifting energy use from peak to off-peak times.
Empowering Energy Storage
Energy storage is at the heart of our transition to a sustainable energy future. A variety of advanced technologies (refer to Post 1) are enabling us to efficiently harness renewable energy and transform how we consume power. Here's how energy storage is reshaping the future.
Optimizing Renewable Energy Usage

Energy storage systems optimize renewable energy usage by storing surplus power from sources like solar and wind when production is high. This stored energy can then be released during periods of low generation, ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply. By balancing the intermittent nature of renewable energy, storage solutions improve grid stability, reduce dependency on fossil fuels, and enhance the efficiency and sustainability of renewable energy systems in meeting the demand.
Reliable Backup Power
Energy storage solutions, such as battery systems and pumped hydro storage, offer reliable backup power during outages, ensuring that homes and businesses remain operational. By storing energy when demand is low, these systems can quickly discharge power when the grid is down, providing stability and continuity of service. This capability is crucial for maintaining operations in critical sectors and enhancing resilience to power disruptions, making energy storage an essential component of modern, reliable power infrastructure.
Reducing Grid Dependence

Technologies like thermal and compressed air storage are key in reducing grid dependence, particularly in areas with unstable power networks. These systems store surplus energy locally, providing a reliable backup and reducing the need to rely on distant or vulnerable grid infrastructure. By decentralizing energy supply, they improve resilience and ensure a more stable power supply, even during outages or when the grid faces fluctuations. This helps to create a more self-sufficient and reliable energy system, especially in regions where grid stability is a challenge.
Maximizing Carbon Footprint

By supporting the integration of clean energy sources like solar and wind, energy storage solutions play a critical role in minimizing carbon footprints. They enable the effective use of renewable energy, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels for backup power and peak demand. By storing surplus clean energy for later use, these systems help to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global efforts toward achieving net-zero targets. This shift toward cleaner, more efficient energy storage systems accelerates the transition to sustainable, low-carbon energy solutions.
Long-Term Cost Savings

Energy storage systems offer long-term cost savings by lowering electricity bills and reducing reliance on the grid. By storing excess energy during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, businesses and homeowners can use that stored power during peak demand times, avoiding higher energy costs. Additionally, energy storage reduces the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades and mitigates the financial impact of outages. Over time, these systems pay for themselves through these savings while also promoting sustainability by enabling greater use of renewable energy, further decreasing dependence on expensive, carbon-intensive power sources. Harnessing Energy Benefits
From advanced batteries to innovative thermal and compressed air systems, energy storage technologies are critical for a more sustainable and resilient energy future. These solutions are reshaping how we power our world, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and sustainability for generations to come.
Powering Tomorrow, Sustainably
Energy storage is a cornerstone of a sustainable energy future, addressing challenges like renewable intermittency and redefining how we consume power.
At VEM Solutions, our advanced motor/generator technologies play a key role in powering critical systems that support energy transitions. With a focus on efficiency and reliability, we are committed to helping industries drive cleaner energy solutions.
Contact us at sg@vem-group.com for more details.
Source: NES Fircrof

.png?width=300&name=Untitled%20design%20(78).png)

